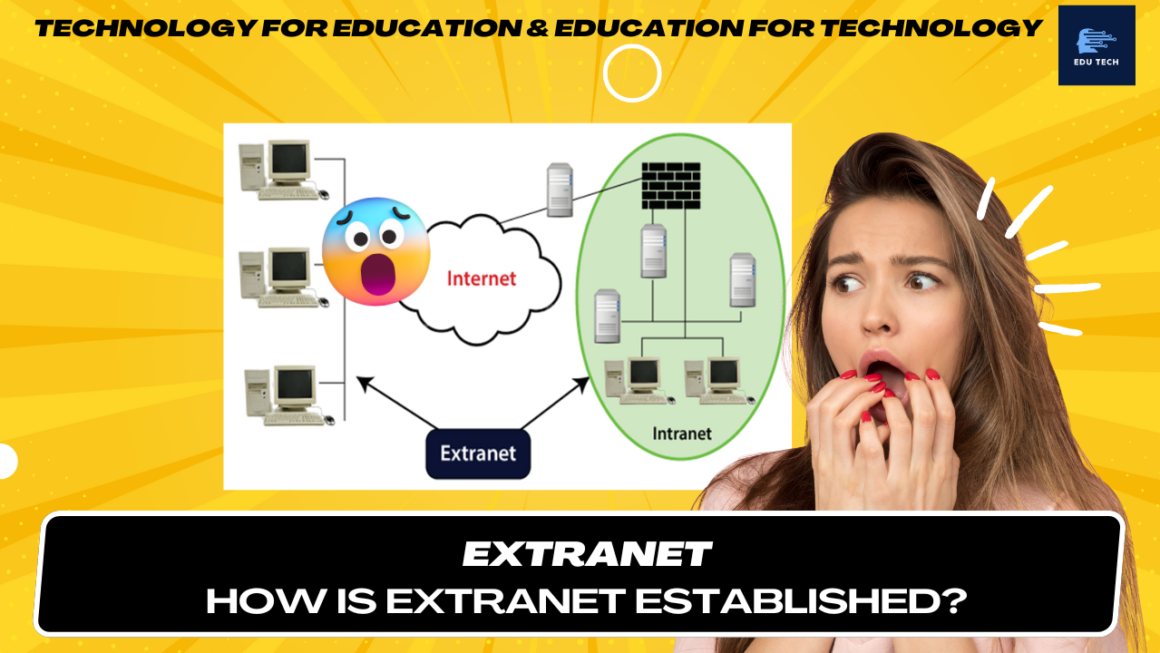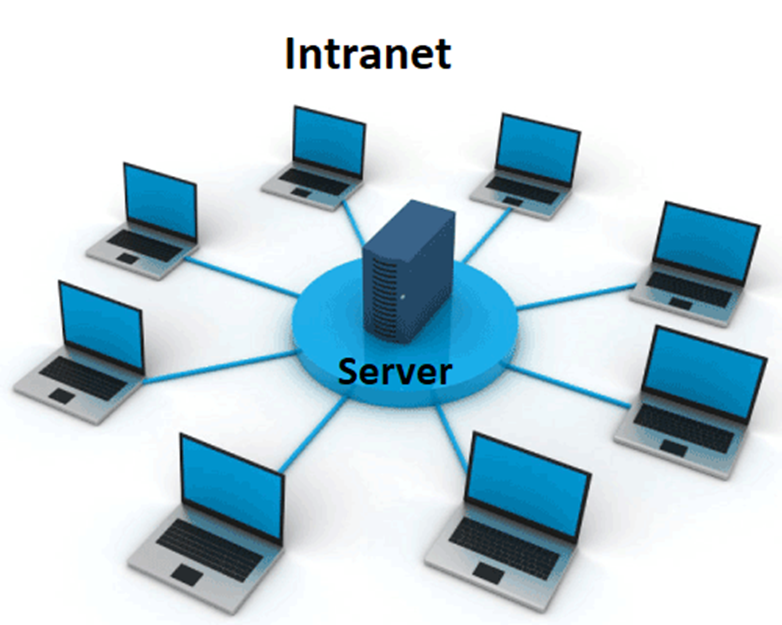
•The intranet is a private network that belongs to a particular organization.
•It is designed for the exclusive use of an organization and its associates, such as employees, customers, and other authorized people.
•It offers a secure platform to convey information and share data with authorized users.
•Confidential information, database, links, forms, and applications can be made available to the staff through the intranet.
•So, it is like a private internet or an internal website that is operating within an organization to provide its employees access to its information and records.
•Each computer in intranet is identified by a unique IP Address.
•It is based on internet protocols (TCP/IP) and is protected from unauthorized access with firewalls and other security systems.
•The firewall monitors the incoming and outgoing data packets to ensure they don’t contain unauthorized requests.
•So, users on the intranet can access the internet, but the internet users can’t access the intranet if they are not authorized for it.
•Furthermore, to access the intranet, the authorized user is required to be connected to its LAN (Local Area Network).
Benefits of the intranet:
Some of the benefits of the intranet are:
•It is cheap and easy to implement and run, and is more safe than the internet and extranet.
•It streamlines communication that enables the company to share its data, information, and other resources among employees without any delay. The entire staff can receive company’s announcements, ask questions, and access internal documents.
•It provides a secure space to store and develop applications to support business operations.
•It improves the efficiency of the company by speeding up workflow and reducing errors.
•Thus, it helps achieve targets by completing the tasks on time.
•It offers a testing platform for new ideas before they are uploaded on the company’s internet webpage.
•Thus, it helps maintain the credibility of the company Information is shared in real-time, or updates are reflected immediately to all the authorized users.
•Modern intranets also offer a mobile app that allows employees to stay connected on the go.
•It aids in project management and tracking workflow and teams’ progress.
•It can work with mobile devices, which means it can provide information that exists on intranet directly to mobile devices of employees such as phones, tablets, etc.
•It can also be used to motivate employees, facilitate employee recognition, and to reward them for performing beyond expectations.
Features of intranet
•Intranets are powerful tools that offer various features to enhance internal communication, collaboration, and organizational productivity.
•Let’s delve into some key features of an intranet and their benefits in simple language.
•Document Management and Sharing: An intranet provides a centralized repository for storing and sharing documents.
•It enables employees to upload, arrange, and access files from a single place.
•Internal Communication Tools: Intranets offer a range of communication tools like messaging systems, discussion forums, and chat platforms.
•These tools facilitate quick and efficient communication between team members, departments, and even across different office locations.
•Employee Directories and Profiles: Intranets often include employee directories and profiles, which serve as digital databases of staff information.
•Employees may search for their coworkers’ contact information, areas of specialization, and job titles to simplify identifying the correct person for the job.
•Task and Project Management:
•Intranets provide tools for managing tasks and projects.
•They enable teams to create and assign tasks, set deadlines, track progress, and share project-related documents and updates.
News and Announcements:
•Intranets often have a dedicated section for news and announcements.
•This feature lets Organizations share company-wide updates, important news, policy changes, or event details.
Collaboration Spaces and Wikis:
•Intranets may include spaces or wikis where teams can collaborate on specific projects, share knowledge, and create a collective knowledge base.
How the Intranet Works:
•Intranet basically comprises three components: a web server, an intranet platform, and applications.
•The web server is hardware that contains all the intranet software and data.
•It manages all requests for files hosted over the server and finds the requested files and then delivers it to the user’s computer.
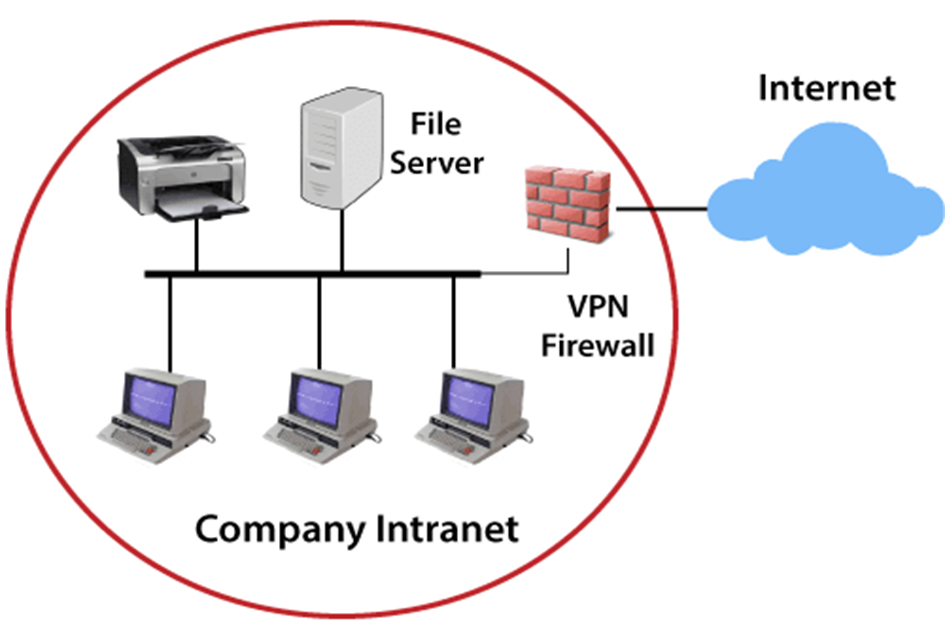
•The intranet platform, which is software, allows communication tools, collaboration apps, and databases to work seamlessly with each other.
•It is tailored to the specific needs of a business.
•The applications are required to enable users to work smoothly.
•They are the computing tools that allow users to do their work, communicate, and coordinate with each other and retrieve and store information.
•Furthermore, the user who wants to access the intranet is required to have a special network password and should be connected to the LAN.
•A user who is working remotely can gain access to the intranet through a virtual private network (VPN) that allows them to sign in to the intranet to access the information.
Types of Intranets
•Several intranet types are available to meet organizations’ unique requirements and preferences.
•Let’s investigate the various intranet types.
Corporate Intranet:
•A corporate intranet is the main platform for internal communication and cooperation inside a firm.
•It gives employees access to internal materials, including corporate news, guidelines, and records.
•Corporate intranets often feature tools for internal messaging, file sharing, project management, and employee directories.
•They foster a centralized hub for employees to stay informed, collaborate on projects, and access essential information about their roles.
Departmental Intranet:
•Departmental intranets are made to meet the needs of certain teams or departments inside an organization.
•They provide specialized features and resources to meet the demands of a certain department, such as sales, marketing, or human resources.
•These intranets allow departments to have dedicated communication channels, document repositories, and collaboration tools, enabling streamlined workflows and focused collaboration within the department.
Enterprise Intranet:
•An enterprise intranet connects multiple organizations or subsidiaries within a larger corporate structure.
•It provides a platform for sharing information, resources, and knowledge across different entities.
•Enterprise intranets facilitate collaboration, coordination, and alignment of processes and strategies among different organizations or subsidiaries within the same corporate umbrella.
Virtual Private Intranet (VPN):
•Remote workers can safely access an intranet’s internal resources via a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
•The data transmission between the remote user and the intranet server is encrypted when a VPN establishes a secure connection over the internet.
•This guarantees that private information is kept secure and private when workers are working remotely for the company.
Extranet-Enabled Intranet:
•An extranet-enabled intranet extends access to external parties, such as clients, partners, or vendors, to specific intranet sections with proper authorization.
•This type of intranet allows external stakeholders to collaborate, access shared documents or project information, and participate in discussions while maintaining control over the information they can access.
•Extranet-enabled intranets enhance collaboration with external parties, fostering stronger business relationships and streamlined workflows.
Cloud-Based Intranet:
•A cloud-based intranet is accessed via web browsers or specific apps and is hosted on a cloud computing platform.
•It provides scalability, flexibility, and remote access options. Intranets built on the cloud do not require on-site infrastructure or maintenance.
•They let employees access the intranet from any device with an internet connection, making them the perfect solution for organizations with geographically distributed teams and remote work circumstances.
Uses of Intranet
•An intranet is a versatile tool that offers several uses to organizations, improving internal communication, collaboration, and productivity.
•Let’s elaborate on the key uses of an intranet in simple language:
Sharing Organizational Updates:
•An intranet provides a centralized platform to share important news, announcements, and updates within the organization.
•It updates staff members on corporate news, policy modifications, new projects, and other pertinent information.
•This promotes openness and alignment while ensuring staff are aware of the most recent changes.
Storing Files:
•One of the primary uses of an intranet is to serve as a central repository for storing and organizing files and documents.
•It allows employees to access important resources, manuals, procedures, and policies whenever needed.
•This feature eliminates the hassle of searching through physical documents or multiple file-sharing platforms, enabling efficient information retrieval and consistency in document management.
Connecting Employees:
•An intranet acts as a digital hub that connects employees across different departments, teams, and locations within the organization.
•It provides employee directories and profiles, making it easier for employees to find and connect with colleagues possessing specific skills or expertise.
•This fosters collaboration, knowledge sharing, and community among employees, even in large organizations with dispersed teams.
Collaborating with Teams Across Borders:
•Intranets facilitate seamless collaboration and project management among teams, irrespective of geographical boundaries.
•Team members can collaborate on documents, share updates, assign tasks, and track progress using dedicated collaboration tools within the intranet.
•This enables efficient teamwork, enhances coordination, and reduces communication barriers, particularly in organizations with remote or globally distributed teams.
Increasing Productivity:
•By providing easy access to information, resources, and tools, an intranet boosts employee productivity.
•It also eliminates the need to search for information across different platforms or rely on time-consuming manual processes.
•Employees can find and share information quickly, access necessary documents, and collaborate effectively, improving efficiency and time savings.
Giving Employees a Voice in the Organization:
•An intranet can include discussion forums, surveys, and feedback mechanisms that empower employees to share their opinions, ideas, and suggestions.
•This gives workers a voice within the company, promotes diversity, and encourages innovation and continual development.
•Employee participation and happiness increase when staff members participate in conversations, provide feedback and participate in decision-making.
Disadvantages of Intranet:
•It may be costly to set up an Intranet due to hidden costs and complexity.
•If the firewall does not work properly or not installed, it can be hacked by someone.
•High-security passwords are required, which cannot be guessed by outside users.
•There is always a fear of losing control over the intranet.
•Sometimes document duplication may happen which can cause confusion among employees.
•You have to give access to multiple users, so you may find it hard to control this network.
•An intranet’s setup and maintenance may be challenging and require IT help.
•Employees may need help in training and adopting the system.
•Managing content can be difficult, leading to out dated information.
•Security breaches and malware attacks are potential risks to be aware of.
•Remote employees may have limited access.
•Regular maintenance is needed to keep the intranet running smoothly.
Examples of Intranet:
Educational Intranet:
•It is generally found in a school, college, etc., For example, a school intranet is intended to allow teaching staff to communicate with each other and get information about upcoming updates such as exam dates, schools functions, holidays, etc.
Real Estate Intranet:
•The intranet of a real estate company allows its sales team to have access to all important brochures, templates, forms that they may need to close a sale.
•Employees also remain up to date with important events like meetings, training, sessions, etc.
•It can also be used to share motivational messages with the team.
Health Care Intranet:
•In the healthcare sector, in big hospitals, the Intranet helps health care professionals to work as a team to provide proper care and treatment to their patients.
•Doctors can share reports, treatment procedures, bills and claims can be settled easily without moving from one department to another department.
IT Sector Intranet:
•In the IT sector three is always a lot of information that needs to be shared with all the employees at one go.
•It may be related to a project that needs to be completed within the given time frame, such as guidelines, terms and conditions, and rules that are to be followed while working on a project.
Difference between Intranet and Internet
| Internet | Intranet |
| It is a medium such as optical fiber cable that connects billions of computers with each other to establish a worldwide network. | It is a small, private network as it belongs to a specific organization. |
| It has billions of users as it is a public network with a worldwide presence. | It has limited users. |
| It is not as safe as an intranet. | It is a safer network than the internet. |
| It can be assessed or used by anyone using an internet-enable devices, such as laptop, mobile phone, etc. | Only authorized persons can use this network. |
| It offers a wide range of information, such as news, blogs, websites, etc. | It offers limited information related to its organization’s work, policies, updates, etc. |
| It is not owned by a single person or an organization. | It can be owned by a person or an organization. |
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Can a remote user access an intranet?
•Remote employees can access the intranet from locations other than the organization’s physical premises if the proper setup and security measures are in place, such as virtual private network (VPN) connections or cloud-based solutions.
•This allows them to access the intranet and use its features.
How secure is an intranet?
•A secure intranet may be achieved with the right security measures in place.
•These include access restrictions, firewalls, encryption, and frequent vulnerability assessments.
•Organizations may protect their intranet against illegal access and potential security breaches by following these protections.
What kinds of information are available on an intranet?
•Various kinds of information may be found on an intranet.
• It frequently contains employee directories, document repositories, project management tools, internal communication channels, collaborative spaces, and business news and updates.
• It is a centralized platform for exchanging and accessing information important to company personnel.
Is training required to use an intranet?
•Depending on the complexity of the intranet and employees’ familiarity with similar systems, some training may be necessary.
•This ensures that employees can effectively use the intranet’s features and functionalities.
•Training sessions or documentation can help employees understand how to navigate the intranet, access resources, collaborate with colleagues, and utilize its tools and applications.
Can an intranet integrate with other business systems?
•Yes, an intranet may be integrated with other corporate platforms.
•It may be integrated with tools for project management, customer relationship management (CRM), human resources management systems, and more.
•By streamlining operations and enabling smooth data sharing, this connection makes it simpler for staff members to access and share information across several platforms.
How frequently should an intranet be updated?
•The demands of the organization, as well as the tools and content on the intranet, determine how frequently changes are made.
•Updates must be made often to guarantee information correctness, include new features or functionalities, and fix any security flaws.
•The intranet should be reviewed and updated as needed by organizations as part of a maintenance routine to keep it up-to-date and helpful for users.