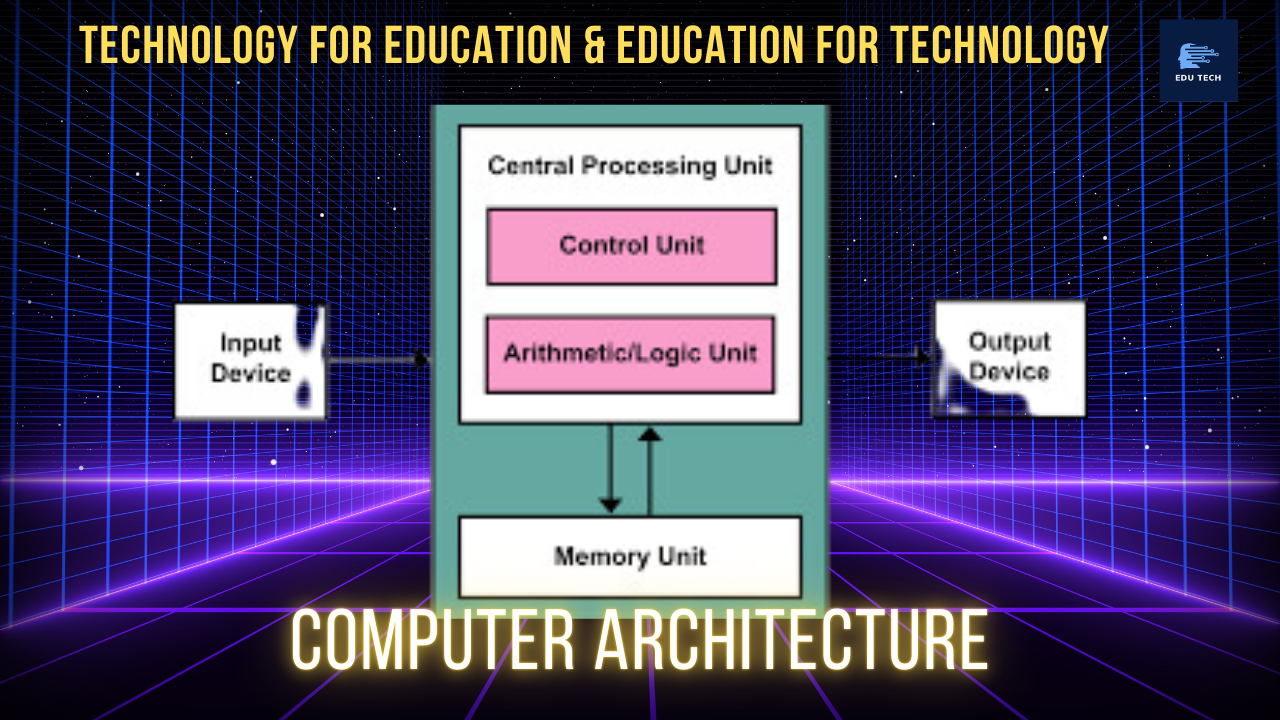
Mr John Von Neumann in 1970 gives some idea on Computer Architecture.
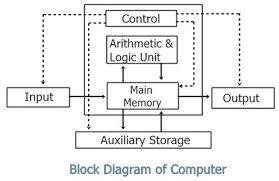
•CU > Input Device > Output Device
•ALU
•Primary Unit
•Secondary Storage
•CU > Control Unit > Arithmetic & Logic Unit
Input Device
The most common input devices are the keyboard, mouse, and touch screen. There are more input devices, like microphones to capture sound waves, scanners to capture image data, and virtual reality devices to capture our body movements.
ASC II
A – 00001
B – 00010
C – 00011
Output Device
Some common examples of output devices are: Monitor/Display, Printer, Speakers, Headphones/Earphones, Projectors, Plotters, Braille Display, Haptic Feedback Device, Digital Signage Display, Touchscreens, etc.
CPU (CU+REGISTER+ALU)
•Transfer instruction & Input date from main memory to register
•Executes the instruction in the stored sequence.
•CPU transfer output data from registers to main memory.
ALU
All arithmetic & logical operations executes.
•Registers
•Data
1) Logical operations
2) Arithmetic operations
3)Bit – shifting operations
4)Comparison operation (=, <. < = >, >=)
CU (Control Unit)
- It controls input device, output device,
- Direct the Computer to Carry out stored program instruction by communicating with the ALU & registers and Organise the processing of date & instructions.
•Fetch the instruction stores stored in main memory.
•Identify the operation.
•The devices involved in it.
•Generate control signals.
Memory Unit
- Temporary & Permanent
Micro processor
•Main Hardware that drive the computers
•Controlling element in a computer system
COMPUTER SYSTEM
Uses in
•Computer
•Calculator
•Any digital system
The speed of CUP depends upon the type of micro processor used in it.
1971 – Intel 4004
•Pentium Series
•i3, i5, i7 series.
MOTHER BOARD
The main Circuit Board
•Main Board
•Logic Board
•System Board
MB
•All the electronic devices
•All the circuits of computer system
- RAM + ROM + Expansion Slots + PCI Slots
- USB Ports + VGA Ports + HDMI Ports
- Controllers for devices (HDD, DVD, Drive, KB, Mouse)
- BIOS
- CMOS Battery
- Buses
Bus
•A Set of wires used for inter connections.
•Each wire can carry one bit of data.
•Electronic signal pathways that allows information & signals.
•Between components inside or outside of a computer.
- Internal Bus & External Bus
Internal Bus
•CPU > System memory System Bus
•Command to access the memory or I/O devices > Control Bus
•Address of I/O devices or memory
•Address Bar
•The data to be transferred
•Data bus
External Bus
> External devices > Peripherals > Expansion slot > I/O ports
> Other (Expansion bus)
Monitor
An image on the monitor is created by configuration of dots,
ØPixels
ØResolution
ØDot Pitch
ØRefreshment Rate – How many times/ sec the display is able to drawn a new image.
Types of Monitor
- Cathode Ray Tube
- Liquid Crystal Display
- Light Emitting Diode
- Thin Film Transistor
PRINTER
CPS > Characters per Second
LPM > Lines per Second
PPM > Pages per Minute
DPI > Dots per Inch
Impact Printer
Printer strikes paper and ribbon together to form a character
ØDot Matrix Printer
ØDaisy Wheel Printer
ØLine Pinter Drum Printer
Non-Impact Printer
Printer uses electrostatic chemicals and inkjet technologies
ØInject Printer
ØThermal Printer
ØLaser Printer
ØElectromagnetic Printer
ØElectrostatic Printer
Input/Output/ 1/0 Port
•External interfaces, used to connect input & output devices.
•1/0 devices are connected to the computer via different ports
ØParallel port
ØSerial port
ØUSB Firewive