•A mouse is a small hardware input device.
•It controls the movement of the cursor on the computer screen and allows users to move and select folders, text, files, and icons on a computer.
•It is an object, which needs to put on a hard-flat surface to use.
•When the users move the mouse, the cursor moves in the same direction on the display screen. The name mouse is derived from its size as it is a small, corded, and elliptical shape device that looks a bit like a mouse.
•A connecting wire of a mouse is imaginable to be the mouse’s tail.
•Additionally, some of the mice have combined features like extra buttons, which may be assigned and programmed with many commands.
•It helps to reduce the use of a keyboard.
Parts of a Computer Mouse
Buttons
•Nowadays, almost every mouse has two buttons, left and right. These buttons are used for manipulating any objects and text as well.
•When a user clicks a button of the mouse, it communicates with the computer to perform an activity on the screen.
•These two buttons (left and right) of the mouse allow users to input different-different messages to the computer, which is based on clicking the left and right-button by users. A computer system understands the left or right-click based on the configuration of your mouse driver.
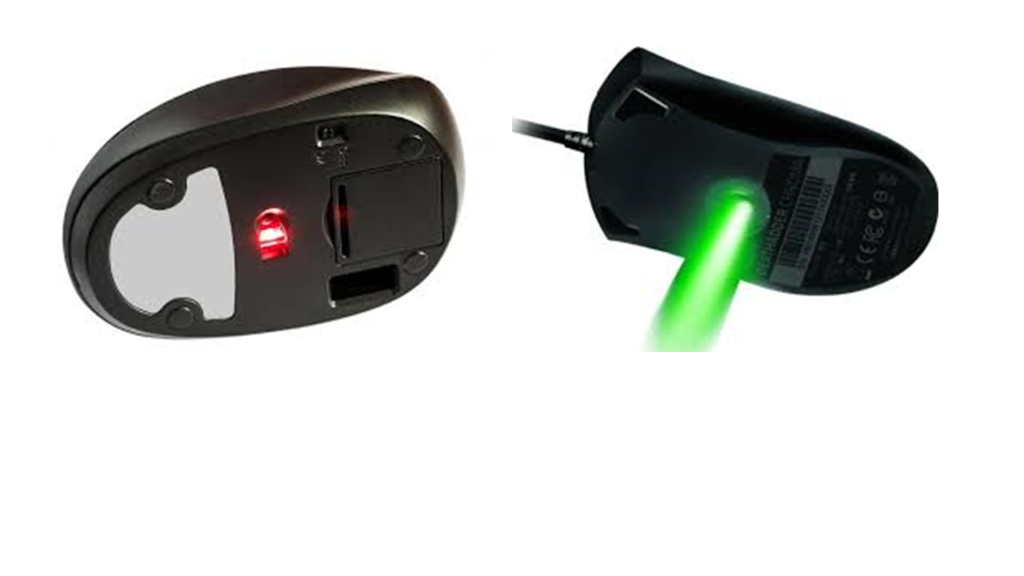
Ball, laser, or LED
•A mouse, if it is a mechanical mouse, uses a ball and rollers, and an optical mouse uses a laser or LED.
•These parts allow the mouse to track the movement on an x-axis and y-axis directions and move the mouse cursor on the screen.
Circuit Board
•A circuit board is located inside of mouse chassis, which is used to transmit all mouse signal information, clicks, and other information.
•This board includes all electronic components such as a diode, register, capacitor, and more.
•It accepts input in the form of electronic signals when a user gives any instruction by clicking the mouse buttons, scrolling, etc.
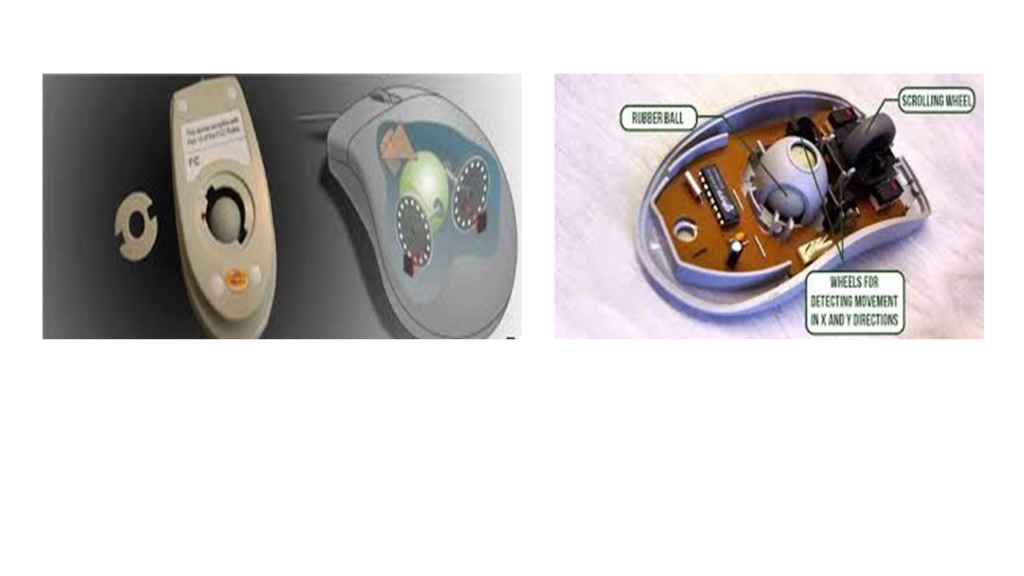
Mouse wheel
Nowadays, computer mouses also include a wheel that is used to scroll the document page up and down direction.
Cable/Wireless Receiver
•The corded mouse has a cable with a plug that connects to the computer.
• If the mouse is wireless, it requires a USB receiver to get the wireless signal, such as (Bluetooth, Infrared, Radio signals), and input it into the computer.
Microprocessor
It is a processor that is embedded on the circuit board of the mouse. All components of the mouse are not able t o work without a microprocessor, as it is the brain of the mouse.
Types of Mouse
•Optical
•Joystick
•Mechanical
•Cordless (Wireless)
•Footmouse
•Touchpad (Glidepoint)
•Trackball
•TrackPoint
•J-Mouse
•IntelliMouse (Wheel mouse)
•Laser Mouse
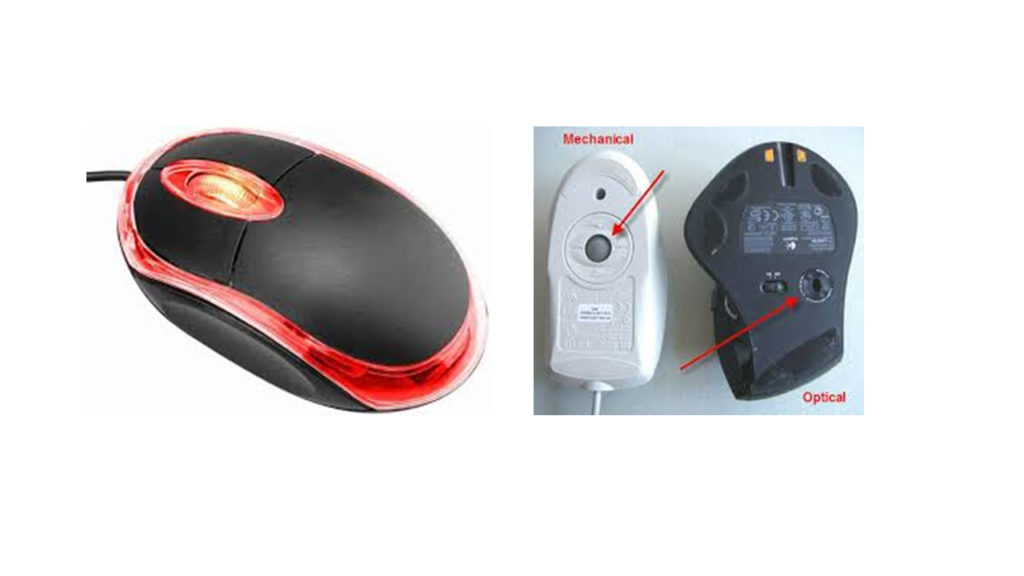
Optical Mouse:
•First introduced by Microsoft on 19 April 1999.
•It tracks movement by using a laser or light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
•It takes microscopic snapshots thousand or more images per second of the working surface.
•The images changes at the time of moving the mouse.
•Instead of interpreting the motion of a rolling sphere, it detects the movement by sensing changes in reflected light.
•It does not require cleaning as it has no moving parts.

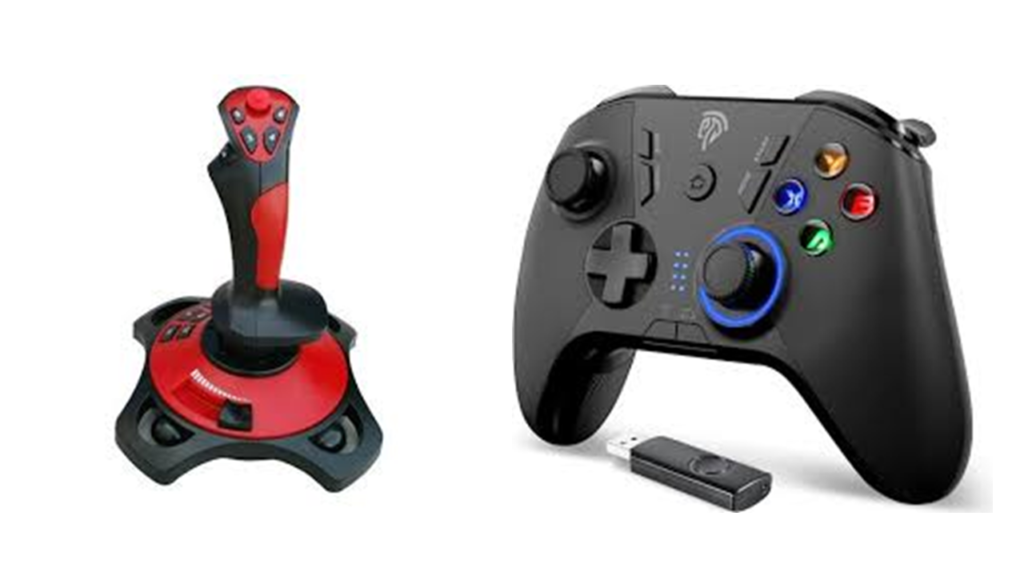
Joystick:
•It is an input device that moves in all directions and controls a machine or a symbol in a computer program.
•It is much like a mouse, except that if you stop to move the mouse, the cursor will also stop. But with the joystick, the pointer does not stop and moves continuously in the direction the joystick has pointed.
•You must need to return the joystick to its upright position for stopping the pointer. Although most of the joysticks have two buttons, which are known as triggers.
•mostly joysticks connect with the computer by using a USB port.
•here are different types of ports that used to connect a joystick such as Bluetooth, Serial Port, USB, Game port.

Mechanical mouse:
•It is a type of computer mouse, also called a ball mouse.
•It consists of a rubber or metal ball on its underside.
•It contains the sensors, when the user moves a mouse in any direction, the sensors inside the mouse detect the movement and move the mouse pointer on-screen in the same direction.
•An optical mouse took the place of the mechanical mouse.
Cordless (wireless) Mouse:
•It is an input device that connects to a computer without any wire.
•With time, wireless technology became popular in the early 2000s, and the wireless mouse started to include Bluetooth, infrared radio waves, and radio frequency technology.
•Commonly, a USB receiver is used to connect the computer with a wireless mouse, which is plugged into the computer and accepts signals from the wireless mouse.
•Wireless mouses require batteries to work that can be AAA batteries, AA batteries, or Li-ion or rechargeable NiMH batteries.

Foot mouse:
•It is a type of computer mouse that provides users the ability to control the mouse pointer or cursor with their feet.
•The reason behind developing this mouse is to enable the users to keep their hands on their keyboard while using a mouse.
•It means a user can use both keyboard and mouse together without interrupting their hands with the foot mouse.
•Also, it is more beneficial for users with disabilities or with neck or high-back problems.

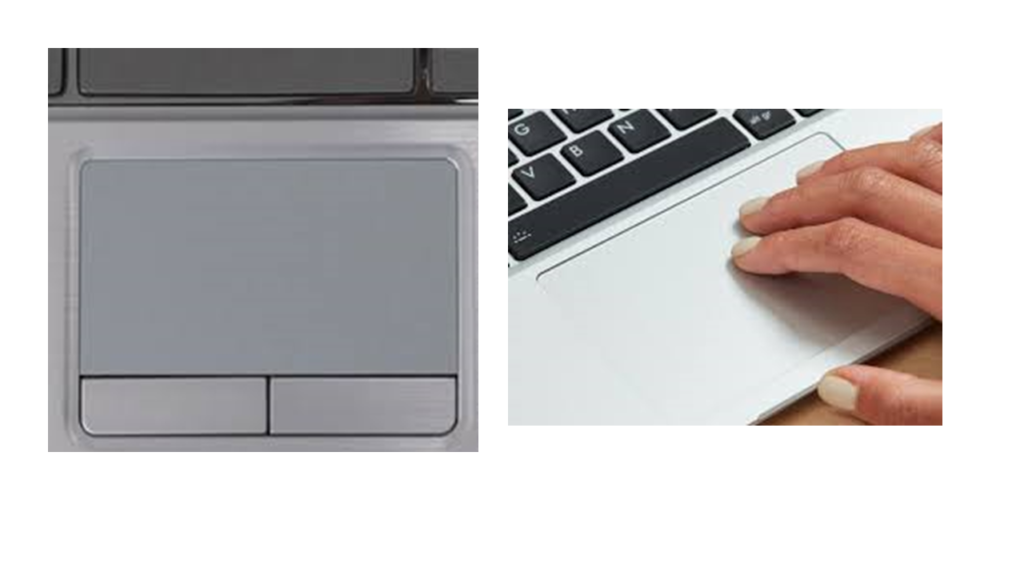
Touchpad:
•It is a flat control surface, also known as a glide point, glide pad, trackpad, or pressure-sensitive tablet.
•It is used to move the cursor by using fingers.
•It is primarily found on laptops and used in place of an external mouse.
•It is designed to be operated with your finger.
•It also includes two buttons under the touch surface like the most computer mouse, which correspond to the left and right-click buttons, respectively.
•Some modern touchpads have multi-touch technology, which allows users to perform different actions by using their multiple fingers on the computer.
•For instance, some programs need to use two fingers to pinch and zoom on an image or a document. You can also use two fingers to rotate an image left or right.

Trackball:
•It is a hardware input device that acts the same function as a mouse, but it includes a moveable ball on the top that allows users to move the cursor in any direction.
•It is designed like an upside-down mouse, which needs less arm and wrist motion as compared to a regular mouse.
•Because, rather than moving the whole mouse, you are only required to roll the moveable ball until with your hand to generate motion input.
•Although trackballs are mainly used with computers, you can also find it in other electronics, like self-serve kiosks, mixing boards, and arcade games.
•These devices commonly include trackballs, which are bigger as compared to ones used with computer input devices.

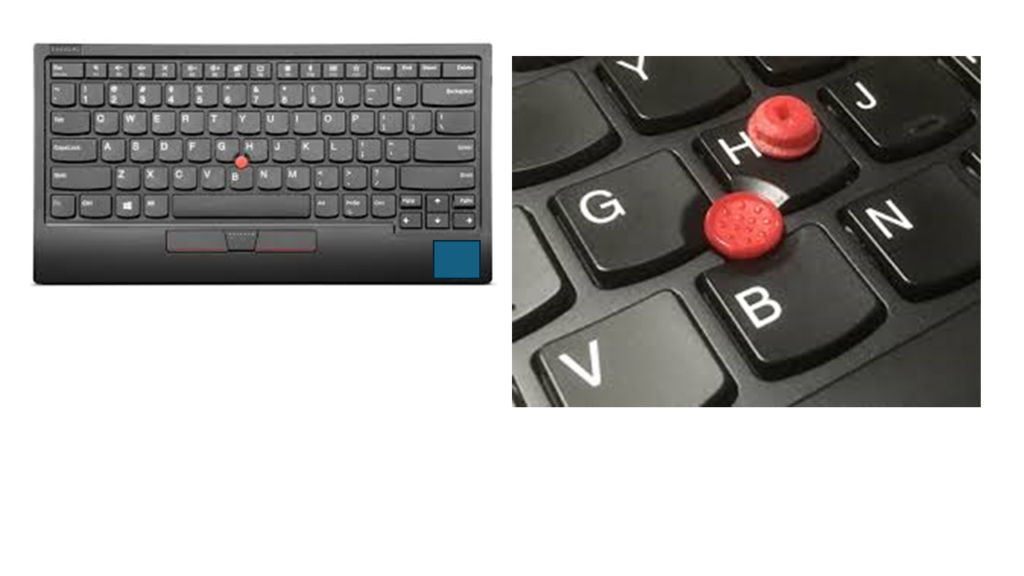
TrackPoint:
•It is a cursor control device, also known as a style pointer, pointing stick, or nub.
•In 1992, IBM introduced the first TrackPoint mouse used with portable computers.
•Sometimes, it is called an eraser pointer, because it looks like a pencil’s eraser head.
•It is located between the “G,” “H,” and “B” keys in the middle of the keyboard.
•This technology allows the users to keep their hands on the keyboard, and they can also control the mouse without interrupting their hands.
•It is operated with the help of pushing in the desired direction where users want to move the cursor.

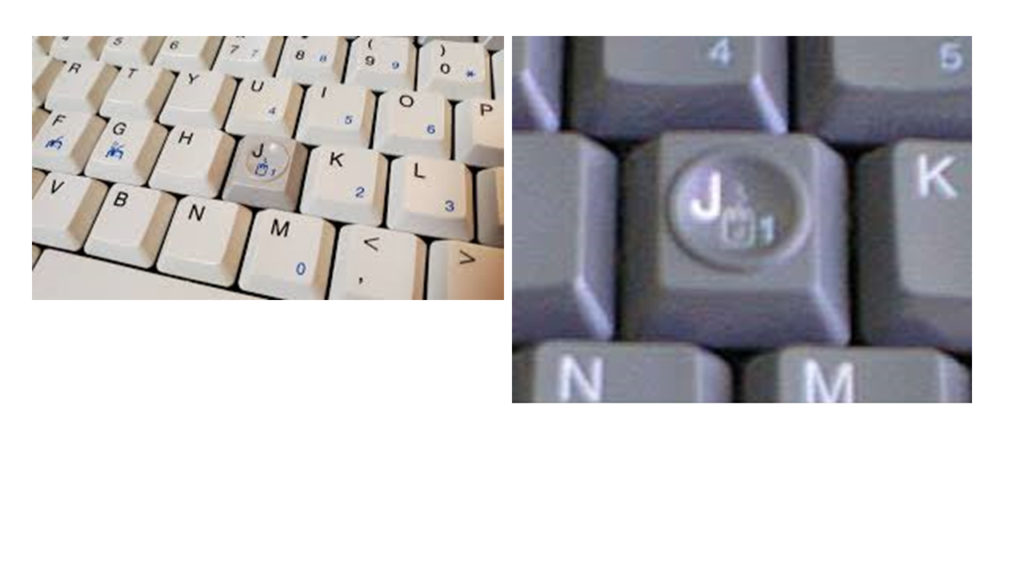
J-Mouse:
•It is another type of mouse that was used with older portable computer devices.
•Like a standard computer mouse, it uses the “J” key from the keyboard to operate the functions.
•Thus, it is known as JMouse.
•It commonly contains two left and right-click buttons under the space bar like some other mouses.
•It is no longer used as it was difficult to use this mouse, and also some better technologies were introduced.

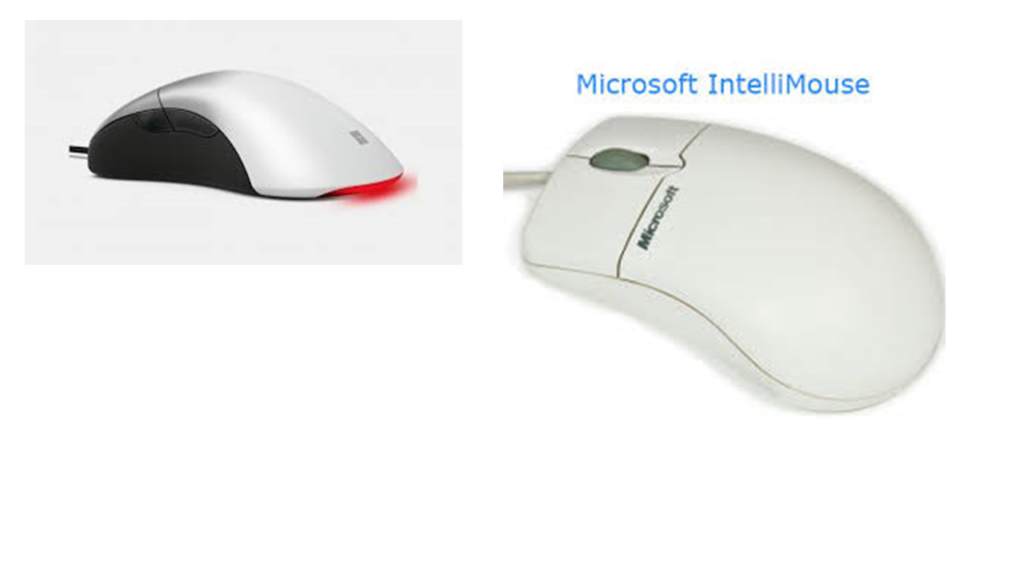
IntelliMouse:
•It was first developed by Microsoft on 22 July 1996.
•It is an optical mouse brand, also known as a scroll mouse or wheel mouse, which includes a wheel between the left and right buttons.
•This wheel is used to scroll up and down a web page. The design of an IntelliMouse was based on the Microsoft Mouse 2.0 from 1993.
•For example, when a user hover on a link and presses down on the mouse wheel, it opens that link to a new tab.
•It has become the standard mouse for most computers as it got wide popularity.
•Furthermore, it is a Microsoft trademark; every mouse manufacturer develops the wheel mouse today.

Laser Mouse:
•A type of optical mouse, laser mouse uses laser light to identify the mouse movement.
•It has no moving parts inside, like all-optical mouse.
•It provides up to 20x greater sensitivity and precision and more appropriate as compared to standard optical mouse design.
•This advanced precision and sensitivity can be useful for graphical or engineering design applications and gaming applications.