•Network devices are electronics devices and required for communication and interaction between hardware devices on a computer network.
•Network devices transfer data in a fast, secure and correct way over same or different networks.
•It may be inter-network and intra-network.
•In this network we see receiver, hosts, data terminal equipment, end system or laptops, mobile phones, routers, servers, etc.
•Devices are connected through cable or wi-fi.

DATA COMMUNICATION
•Data can be any text, image, audio, video and multimedia files.
•And communication is the process of sending or receiving data.
•So the data communication is a process of exchanging data or information or sharing resources between two or more connected devices through the wire or wireless media.
•Now to maintain this process it involves a communication system which is done in combination of hardware and software.
•The hardware part, called nodes are for sending and receiving devices and also intermediate devices.
•And the software part brings certain rules which specify some protocol by which this communication happens.

COMPONENTS OF DATA COMMUNICATION
•Message : It is a piece of information, which is to be transmitted from one point to other in the form of a text file, an audio file, a video file etc.
•Sender : It is for only sending data message, may be a computer, mobile, laptop etc.
•Receiver : It is for receive messages, may be again computer, mobile, laptop etc.
•Transmission Medium/Communication Channels : The medium are used for to connect two or more workstations is called Communication Channels, either by wired media or wireless media.
•Protocol : When sender sends the data, receiver should understand that before acknowledge. So a set of rules are there to make the communication happens within.

HALF DUPLEX COMMUNICATION
•A Walkie-talkie operates in half duplex communication.
•Because it can send or receive a data or transmission at any given time, not both at the same time.
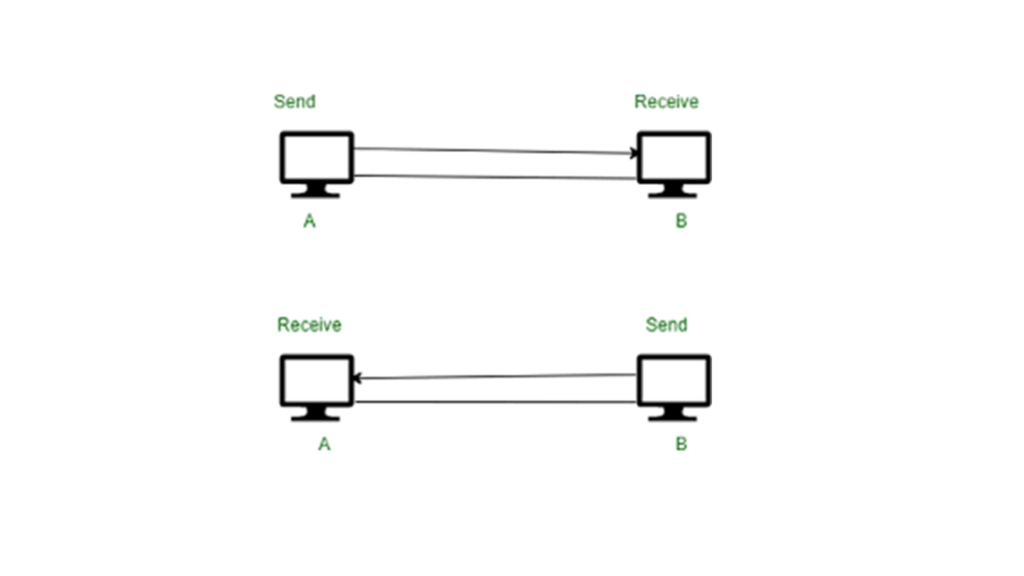
FULL DUPLEX COMMUNICATION
•A full duplex system can transmit data simultaneously in both directions on transmission path.
•Full duplex method is used to transmit the data over a serial communication link.
•Here two wires are required.
•The channel capacity is shared by both communicating devices at all times.
•Telephone networks operates in full duplex communication , here two persons talk on telephone line, both can listen and speak simultaneously.

CABLING AND ITS OPERATAION – COPPER CABLE
•The most common type of cable used in data communication is copper.
•There are different types of copper cable, send the data as an electrical signal.
•The faster the data transfer rate over copper cable the greater the possibility of signal loss and obstruction.
•Though with the development of technology, its reliability is increasing and also minimizing data loss.
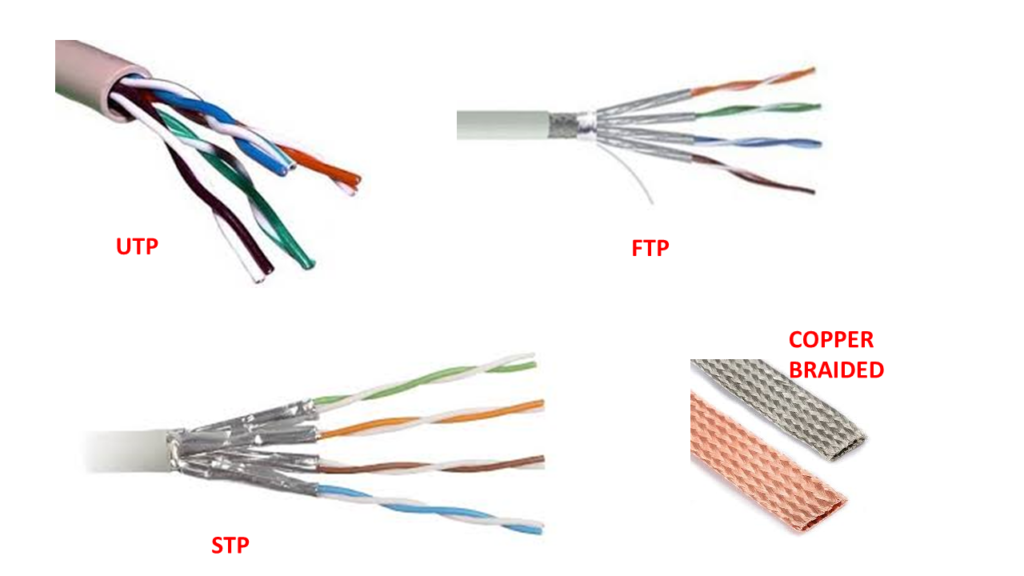
•In wiring, UTP (Unshielded twisted pair), FTP (Foil twisted pair) and STP (Shielded twisted pair) cable type is used.
Twisted Pair :
•The twisting of the pairs of copper cable is the method used to protect the cable’s signals from interference and crosstalk., also called cancellation.
•The more twists the higher quality the cable.
•Again how effective the shielding is depends on the material used for the shield, its thickness and frequency, the type of electromagnetic noise filed, the distance from the noise source to the shield.
•STP is similar to UTP but with each pair covered by an additional copper braid jacket or foil wrapping.
•Category 3 : Is used for data networks using frequencies up to 16 MHz. Popular for telephone and 10 Mbit/s Ethernet networks using TVHV cable type.
•Category 5e : Is used for network up to 100 MHz, for 100 Mbit/s Ethernet networks
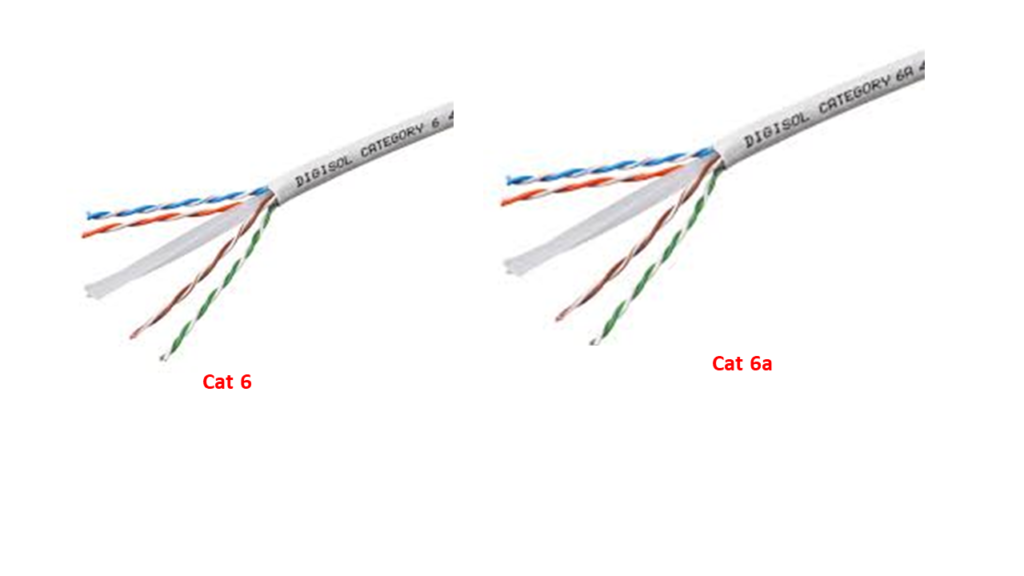
•Category 6 : Is used for up to 250 MHz, more than double category 5e, suitable for 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet networks.
•Category 6a : Is used for up to 500 MHz, double that of Category 6, suitable for 10GBase-T networks.
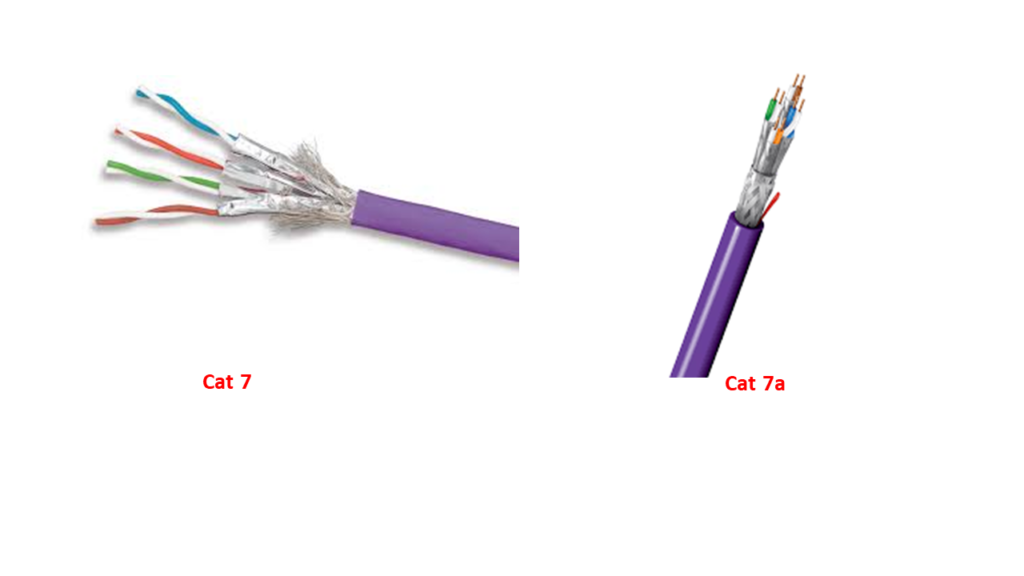
•Category 7 : Is used for networks up to 600 MHz, here four individually- shielded pairs inside an overall shield.
•Category 7a : Is used for network up to 1000 MHz.


Aluminium Wire
•Aluminium wire is also a electrical wire, used for residential construction.
•Aluminium provides better conductivity to weight ration than copper and therefore is used for wiring power grids, overhead power transmission lines and local power distribution line.
•Aluminium is an alternative compared to copper wire cost.
•It is also a poorer electrical conductor compared to copper.
•When electricity flows, it expands more than copper when it heats up.
Coaxial Cable
•Coaxial cable is called “coaxial” because it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis.
•The outer channel is for ground.
•It provides an interference-free transmission path for high-frequency electrical signals.
•ThickNet – It is used with Ethernet 10Base5 network and it covers the distance of up to 500 meters.
•ThinNet – It is much thinner and more flexible type of coaxial cable and used on Ethernet 10Base2 network and covers the distance of up to 185 meters.
•Compared to twisted-pair, coax provides greater bandwidth systemwide, greater bandwidth for each channel.
•So it can support a mixed range of services like Voice, data and even video and multimedia.
•Coax has lower error rates and therefore slightly better performance than twisted-pair.
•Coax cable shielding reduces noise and crosstalk.
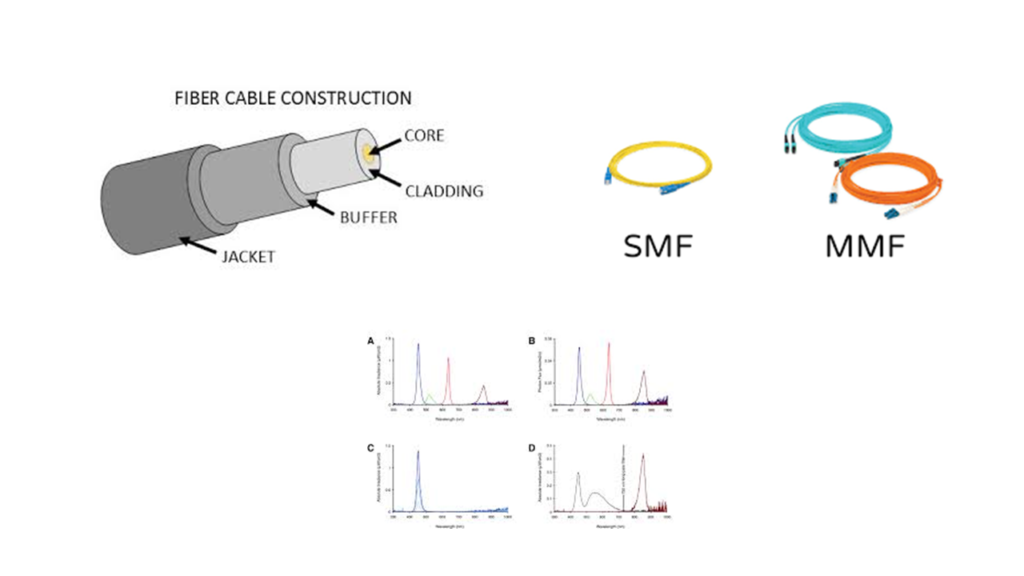
Fiber Optic Cable
•This cable containing one or more optical Fibers that are used to carry light.
•The coating helps protect the Fibers from heat, cold, electromagnetic interference from other types of wiring, and also some protection from ultraviolet rays rom the sun.
•It allows for a much faster data transmission than standard copper wires, because of higher bandwidth.

•It consists of glass or plastic Fibers that carry data in the form of light signals.
•Here only light but no electric signal, like copper wire.
•So the Fiber cable can not be tapped to detect signals.
•It is perfect for high spped and high quality data transmission.
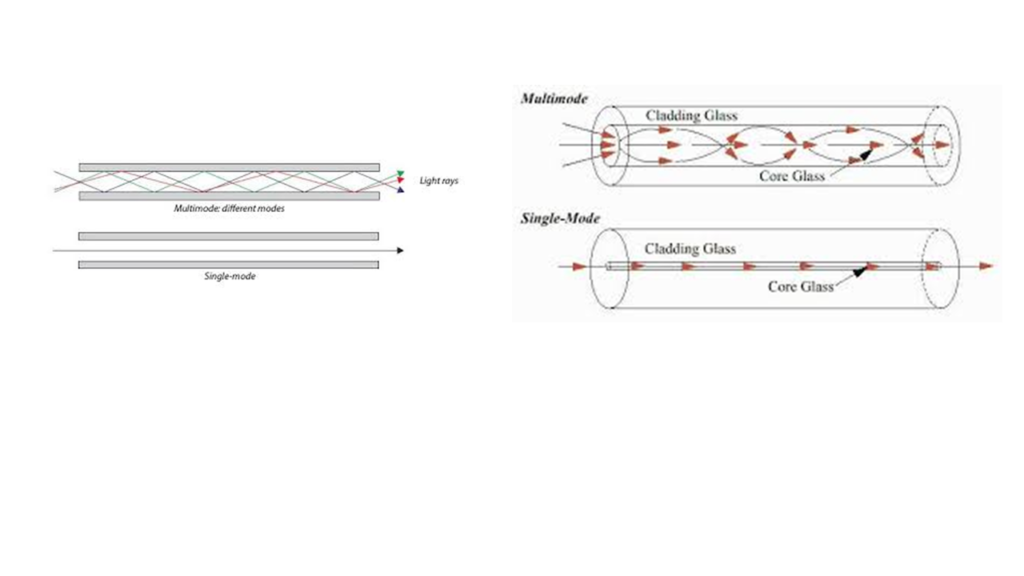
•The reliability, security and distance covered by Fiber optic cable is much greater than copper cable. It is two types, one is single mode cable and other one is multi mode cable.
Single Mode Cable
•It is a single stand (mostly 2 Fibers) of glass Fiber with a diameter of 8.3 to 10 microns (1 micron = one-millionth of a meter and one-thousandth of a millimeter) that has one mode of transmission.
•It is relatively narrow diameter, through which only one mode will propagate.
•It carries higher bandwidth than multimode Fiber but requires a light source with a narrow spectral width.
•It is used in many applications where data is sent at multi-frequency so only one cable is needed.
•It gives a higher transmission rate and up to 50 times more distance than multimode but it cost more.
•Single mode Fiber has a much smaller core than multimode.
•So the small core and single light-wave virtually eliminate any distortion
•Since overlapping of light pulses not seen, it results the least signal attenuation and the highest transmission speed.
Multi Mode Cable –
•It has a little bit bigger diameter, with a common diameters in the 50 to 100 micron range.
•In case of multi mode Fiber, 2 Fiber is used in most application.
•Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is a newer plastic-based cable which gives performance similar to glass cable on very short runs but at a lower cost.
•Multimode Fiber gives high bandwidth at high speeds (10 to 100MBS – Gigabit to 275m to 2km, 1 Gbit/s up to 1000 m, and 10 Gbit/s up to 550 m) over medium distances.
•Typical multimode Fiber core diameters are 50, 62.5 and 100 micro meters.
•In long cable runs (> 3000 feet) multiple paths of light can cause signal distortion at the receiving end.

Advantage of Fiber Optic Cable –
•It has a much greater bandwidth than metal cables.
•In case of longer transmission distance, there is low power losses.
•Longest recommended copper distance is 100m but with Fiber it is 2000m in a network.
•Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference. It can also run in electrically noisy environments without concern as electrical noise will not affect Fiber.
•A Fiber optic cable has nearly 4.5 times as much capacity as the wire cable has compare to copper cable and a cross sectionals area that is 30 times less.
•Since it is a dielectric so it does not present a spart hazard.
•It is difficult to tap since it does not radiate electromagnetic energy. It is most secure medium for carrying sensitive data.















