- Resistor resistance to the circuit and reduces the flow of electrical current.
- Reduce ? Depends on value of Resistor.
- These values are measured in ohms
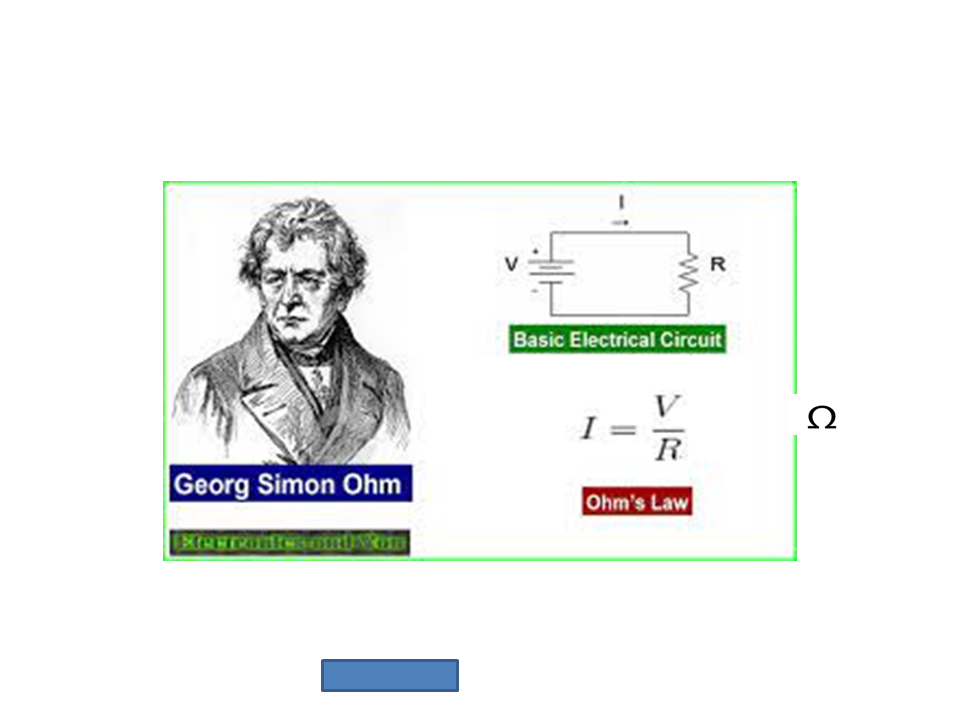
Ohm’s Law
- V = voltage, I = current, R = resistance
- V= 12v, R = 600 Ohm
- I = 12 V/600 Ohm
- I = 0.02 A = 20 mA (milli Ampere)
- So the current in the circuit is 20 mA.
- R = 600 Ohm , I = 3 Ma
- V= 600 x 3 = 1.8 v
- Resistors have different wattage ratings (W = V X I)
- Quarter Watt , Half Watt, 1 Watt, 2 Watt etc.
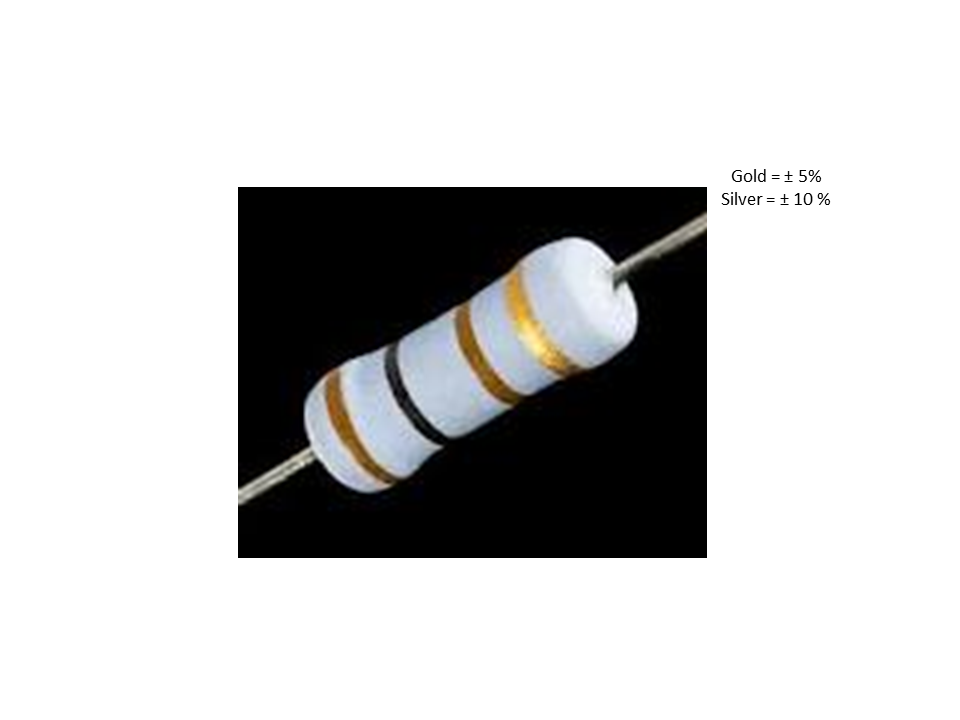
Tolerance of a Resistor
Tolerance = value of resistor x value of tolerance band
Gold = ± 5%
Silver = ± 10 %
None = ± 20%

Types of Resistor
- Carbon
- Wire wound.
- Thin Film .
- Carbon Film.
- Metal Film.
- Thick Film.
- Metal Oxide .
And then
- Variable
- Fixed
And then
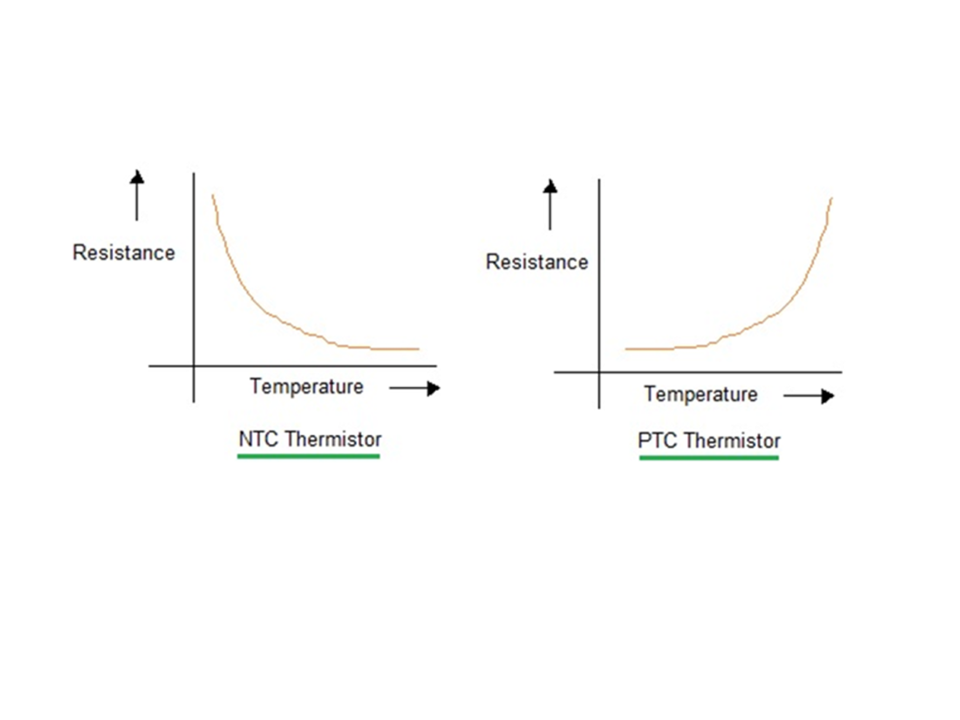
- NTC
- PTC

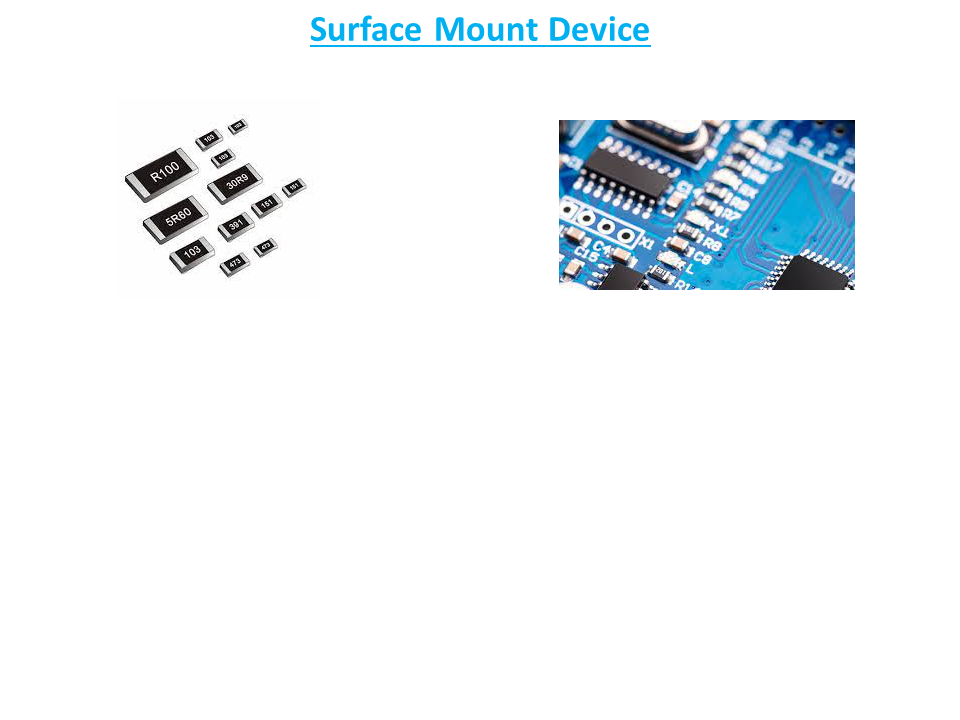
Surface Mount Device
The size of SMD resistors is indicated by a numerical code, such as 0603. This code contains the width and height of the package. So, the imperial code 0603 indicates a length of 0.060″ and a width of 0.030″
Series Vs. Parallel
Series = > R = r1+r2+r3+………rn
Parallel => 1/R = 1/r1 + 1/r2+…..1/rn

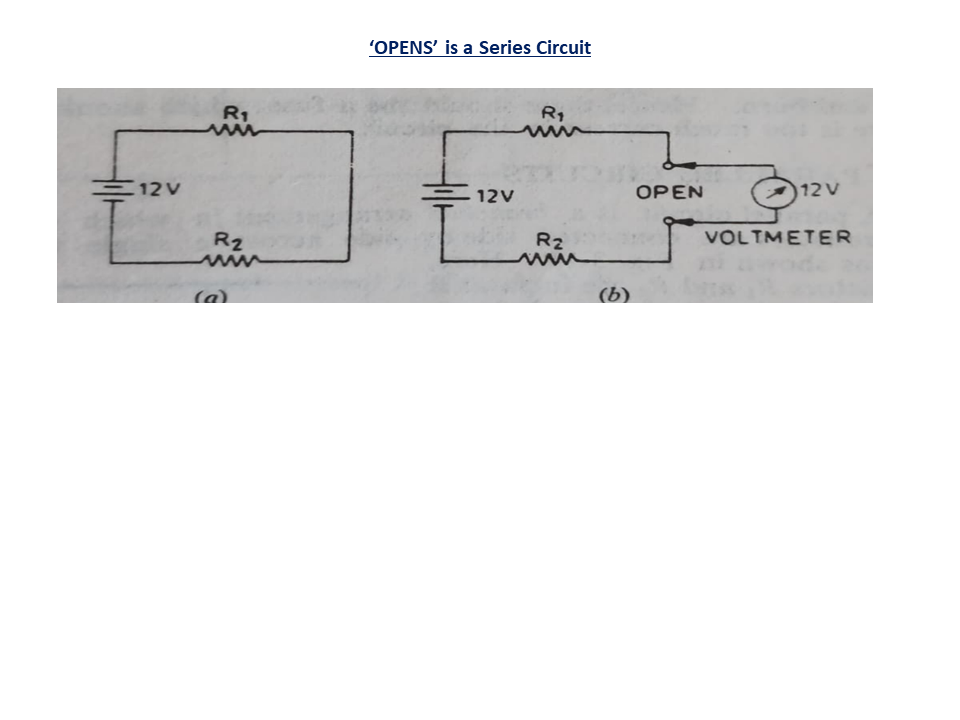

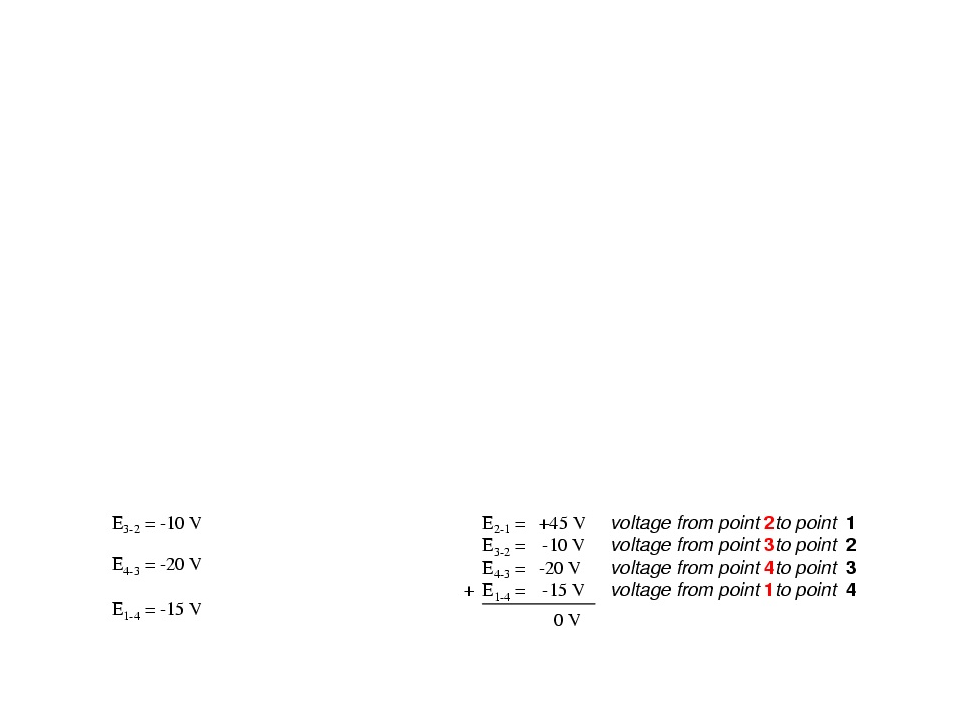
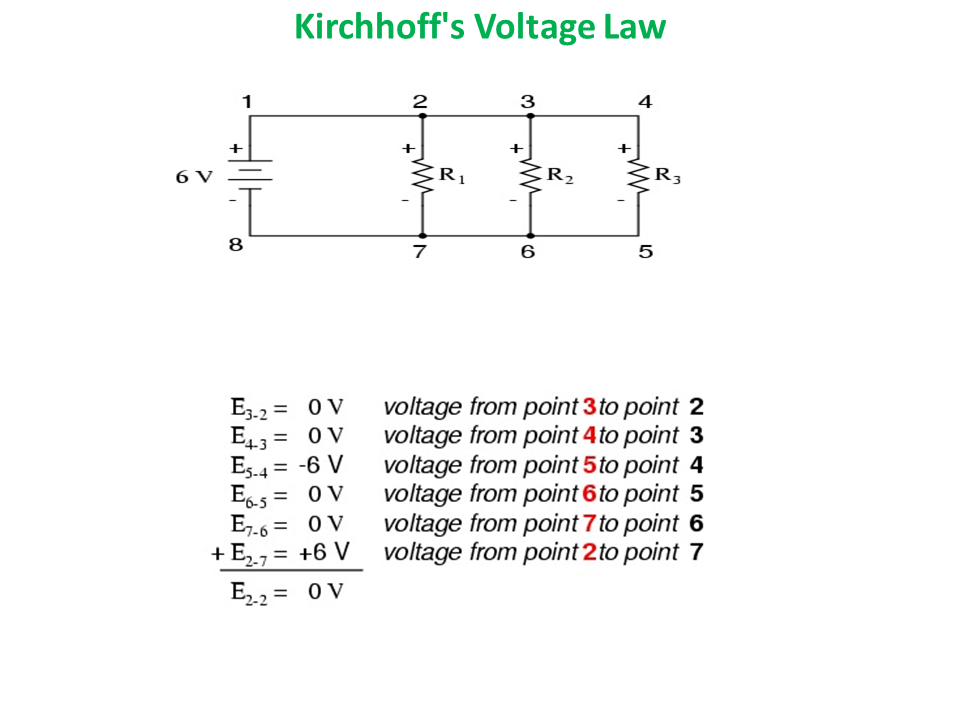
Kirchhoff’s Laws
The voltage around a loop equals the sum of every voltage drop in the same loop for any closed network and equals zero
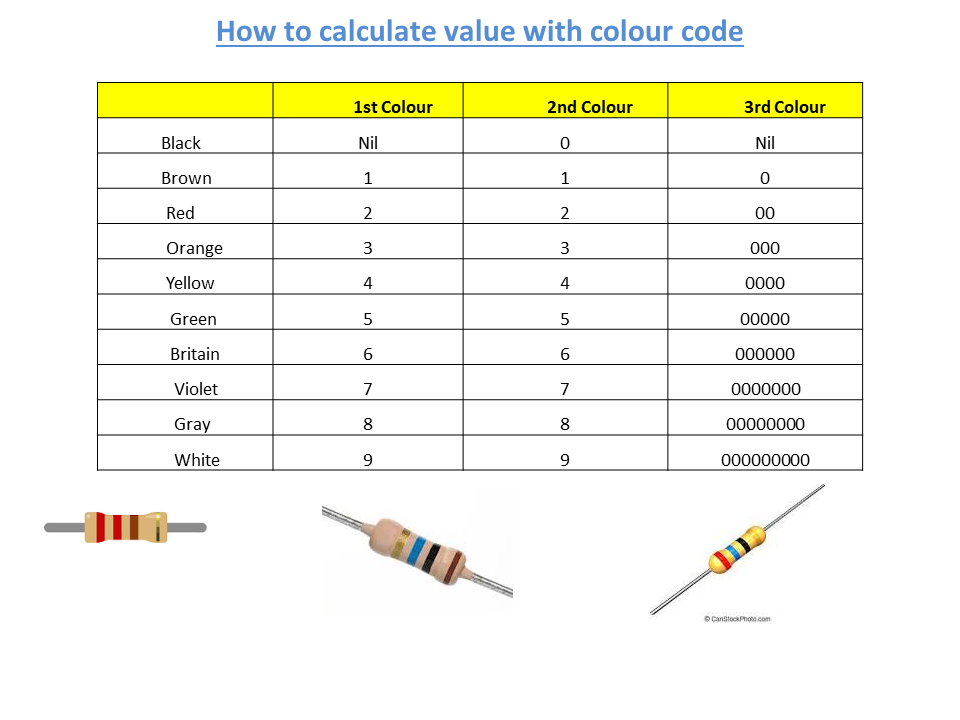
COLOUR CODE
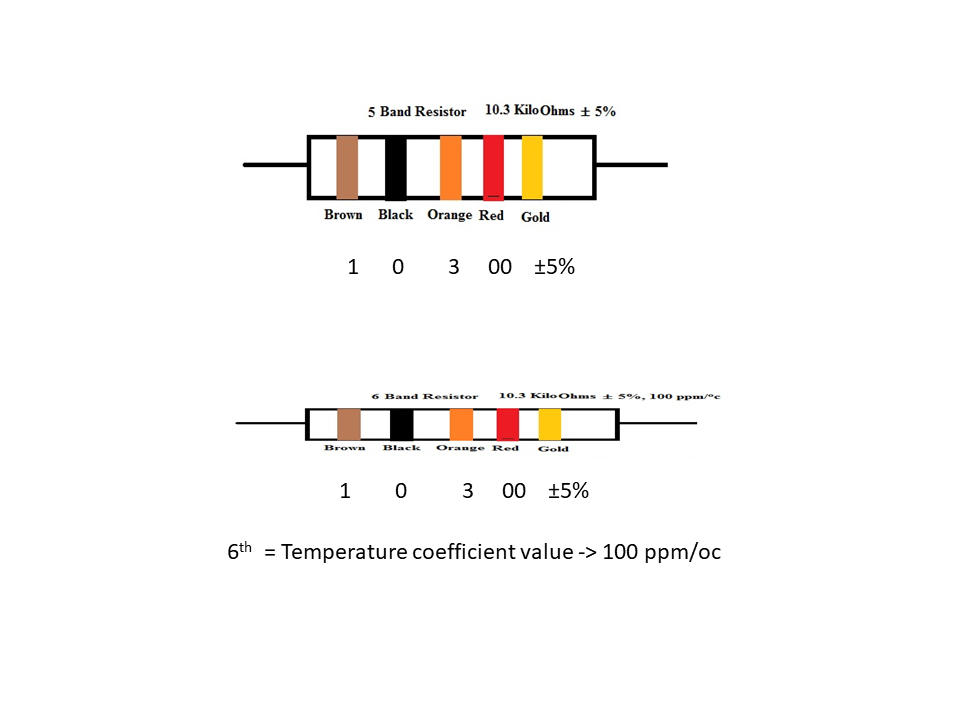
5 Band Resistor Color Code
6 Band Resistor Color Code
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
The algebraic sum of all voltages in a loop must equal zero.